Concept
EnergySense is an iOS mobile application that encourages energy conservation by balancing automation and personal control.
EnergySense is built in iOS and with LittleBits sensors.
Role in Project

Data Collection
Gathered Data from iPhone Sensors including Accelerometer and Microphone

Design and Development of Sleep Sensing Algorithm
Processed collected data to design and implement the sleep sensing algorithm using data structures like Queues in SWIFT.

User Interviews
Conducted user interviews to conclude room-mate conflicts for the lack of energy conservation in shared spaces.
Process
-
How to detect movement?
After researching, I collected acelerometer data along 3 axes - x, y and z- from an iPhone 6 placed in the bed while a person was sleeping. These values were plotted and their averages were calculated. If any real-time data retrieved were greater than the averages, then this would mean that a person is awake.
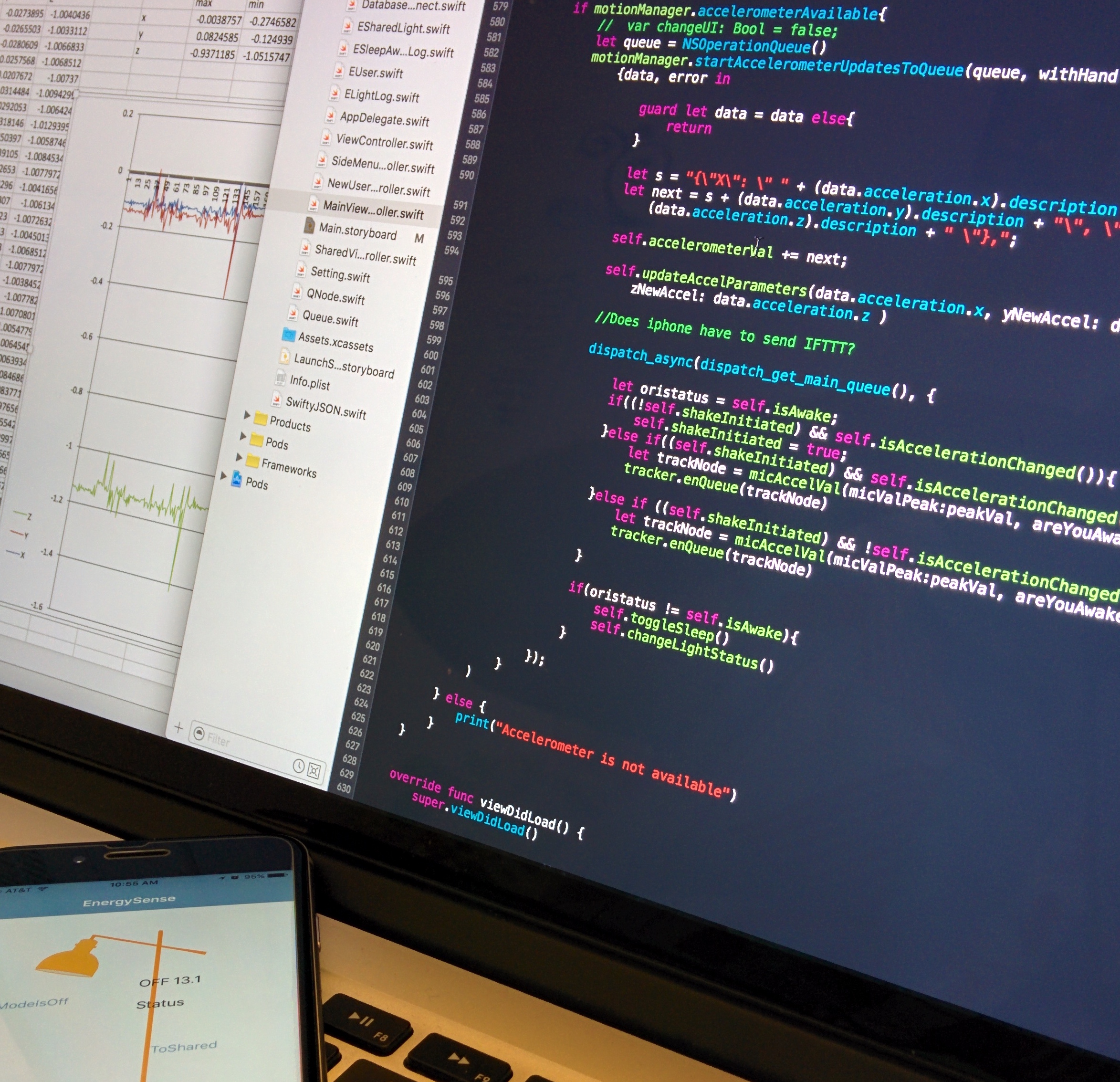
-
Problem Identified - Unable to adapt to users
During testing, fixed values did not account for user's unique behaviors for example tossing and turning intensities. Unique phone cases weren't considered hence resulting in varying axis offset values.
-
Research and Design solution
Thought about 2 solutions:
1) Collect large pools of data to find 'opportunistic' values
2) Considering Android shake algorithms
Due to feasibility, second was chosen that successfully solved the issue of variance among users. -
How to make algorithm more robust?
At this point algorithm could not detect false negatives for example when the phone is idle on the table but user is in a conversation. Hence sound was incorporated, making me collect sound samples of microphone. Like accelerometers, in order to account for varying environment sound levels, I included the calibrate function.
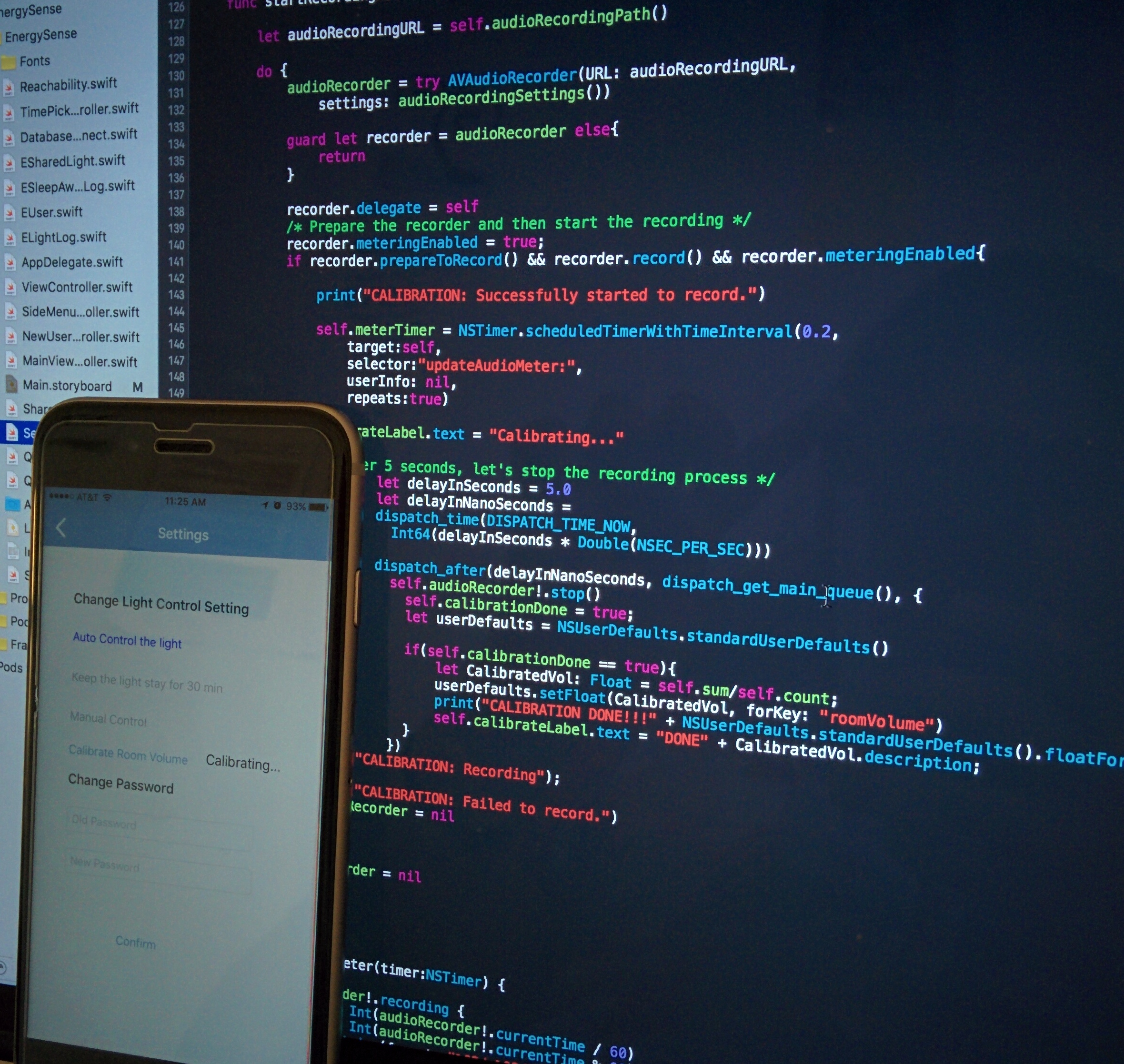
-
Making system sensitive enough
In order to prevent the system for being overly sensitive, a queue was implemented to store values from the accelerometer and the microphone for calculating over a period of 10 seconds to claim if the user is asleep or awake. This prevents the light from responding instantaneously to sensor information.





